350 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
350 lines
15 KiB
Markdown
# 状态管理
|
||
|
||
有状态的计算是流处理框架要实现的重要功能,因为稍复杂的流处理场景都需要记录状态,然后在新流入数据的基础上不断更新状态。下面的几个场景都需要使用流处理的状态功能:
|
||
|
||
- 数据流中的数据有重复,我们想对重复数据去重,需要记录哪些数据已经流入过应用,当新数据流入时,根据已流入过的数据来判断去重。
|
||
- 检查输入流是否符合某个特定的模式,需要将之前流入的元素以状态的形式缓存下来。比如,判断一个温度传感器数据流中的温度是否在持续上升。
|
||
- 对一个时间窗口内的数据进行聚合分析,分析一个小时内某项指标的75分位或99分位的数值。
|
||
- 双流Join场景。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
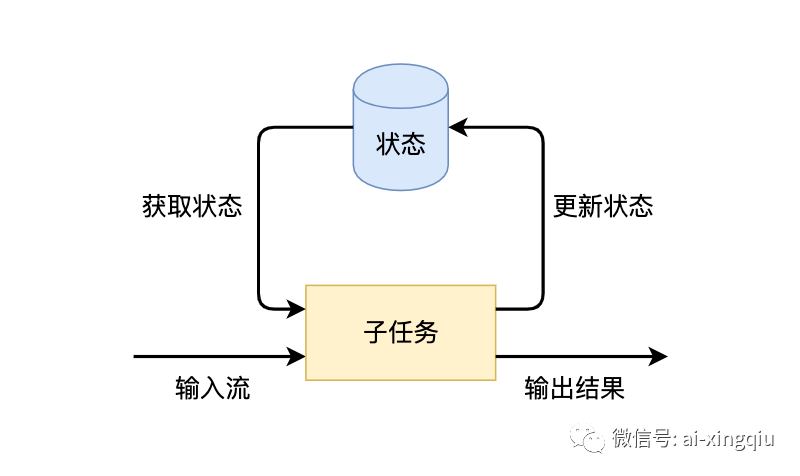
Flink的一个算子有多个子任务,每个子任务分布在不同实例上,我们可以把状态理解为某个算子子任务在其当前实例上的一个变量,变量记录了数据流的历史信息。当新数据流入时,我们可以结合历史信息来进行计算。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Managed State和Raw State
|
||
|
||
Flink有两种基本类型的状态:托管状态(Managed State)和原生状态(Raw State)。从名称中也能读出两者的区别:Managed State是由Flink管理的,Flink帮忙存储、恢复和优化,Raw State是开发者自己管理的,需要自己序列化。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
| - | Managed State | Raw State |
|
||
| :----------- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ----------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||
| 状态管理方式 | Flink Running托管,自动存储、自动恢复、自动伸缩。 | 用户自己管理 |
|
||
| 状态数据结构 | Flink提供的常用数据结构,如:ValueState、ListState、MapState等。 | Raw State只支持字节,任何上层数据结构需要序列化为字节数组。 |
|
||
| 使用场景 | 绝大部分算子 | 自定义算子 |
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### Managed State
|
||
|
||
对Managed State继续细分,它又有两种类型:Keyed State和Operator State。
|
||
|
||
#### Keyed State
|
||
|
||
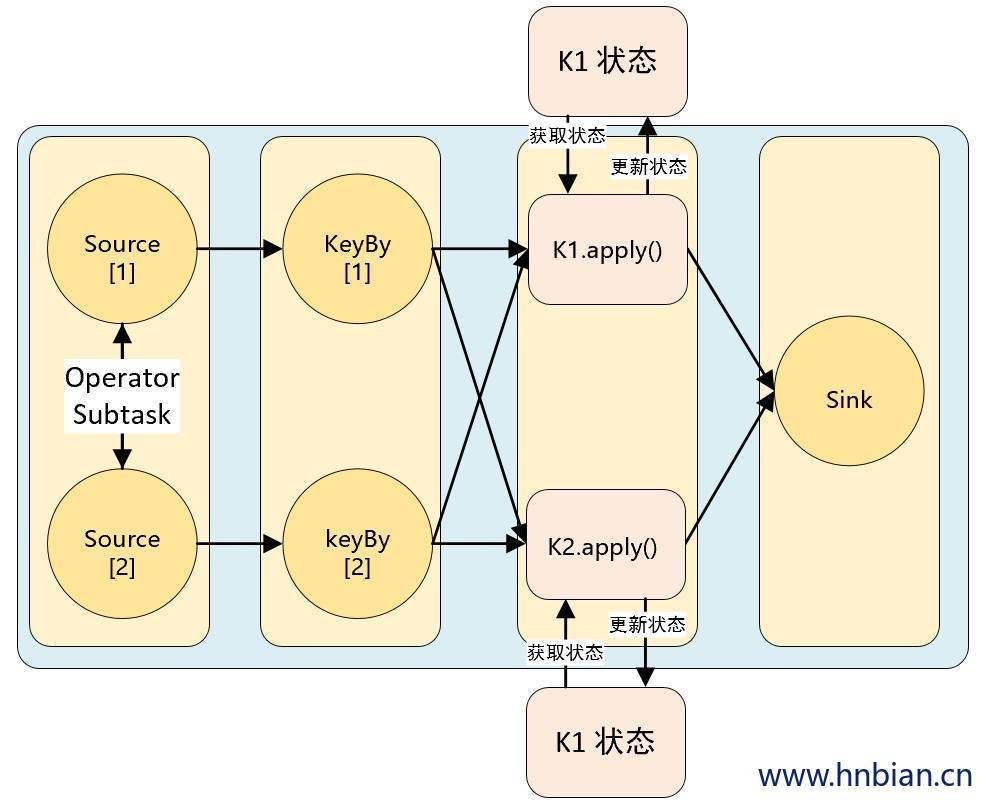
Flink 为每个键值维护一个状态实例,并将具有相同键的所有数据,都分区到同一个算子任务中,这个任务会维护和处理这个key 对应的状态。当任务处理一条数据时,它会自动将状态的访问范围限定为当前数据的 key。因此,具有相同 key 的所有数据都会访问相同的状态。Keyed State 很类似于一个分布式的 key-value map 数据结构,只能用于 KeyedStream( keyBy 算子处理之后)。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Keyed State 有五种类型:
|
||
|
||
- ValueState :值状态,保存单个类型为 T 的值。
|
||
- ListState :列表状态,保存一个类型为 T 的列表。
|
||
- MapState :映射状态,保存 Key-Value 对。
|
||
- ReducingState :聚合状态。
|
||
- AggregatingState:聚合状态。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
#### Operator State
|
||
|
||
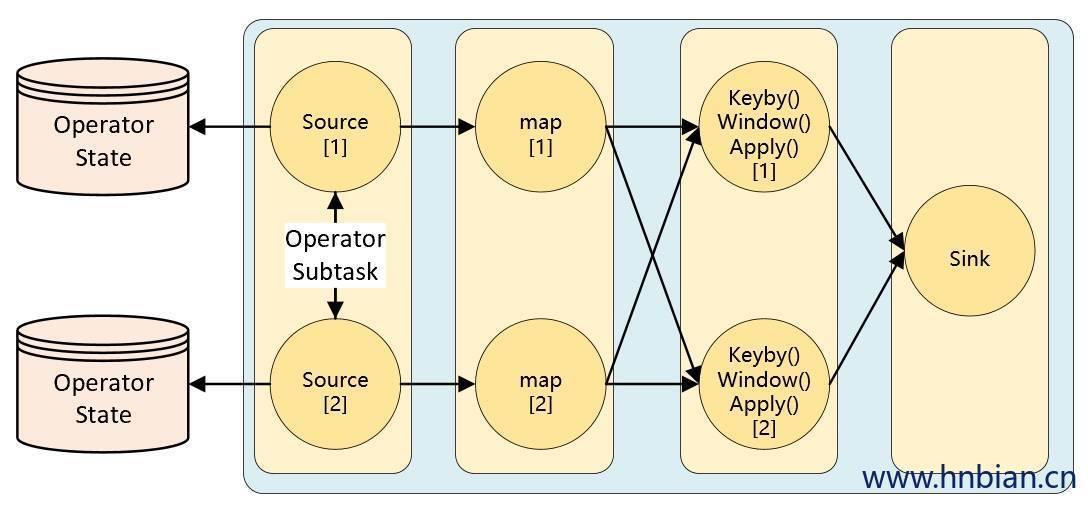
KeyedState 是在进行 KeyBy 之后进行状态操作时使用的状态类型,那么像 Source、Sink算子是不会进行 KeyBy 操作的,当这类算子也需要用到状态,应该怎么操作呢?这时候就需要使用 Operator State(**算子状态**)Operator State 是绑定在 Operator 的并行度实例上的,也就是说一个并行度一个状态。
|
||
|
||
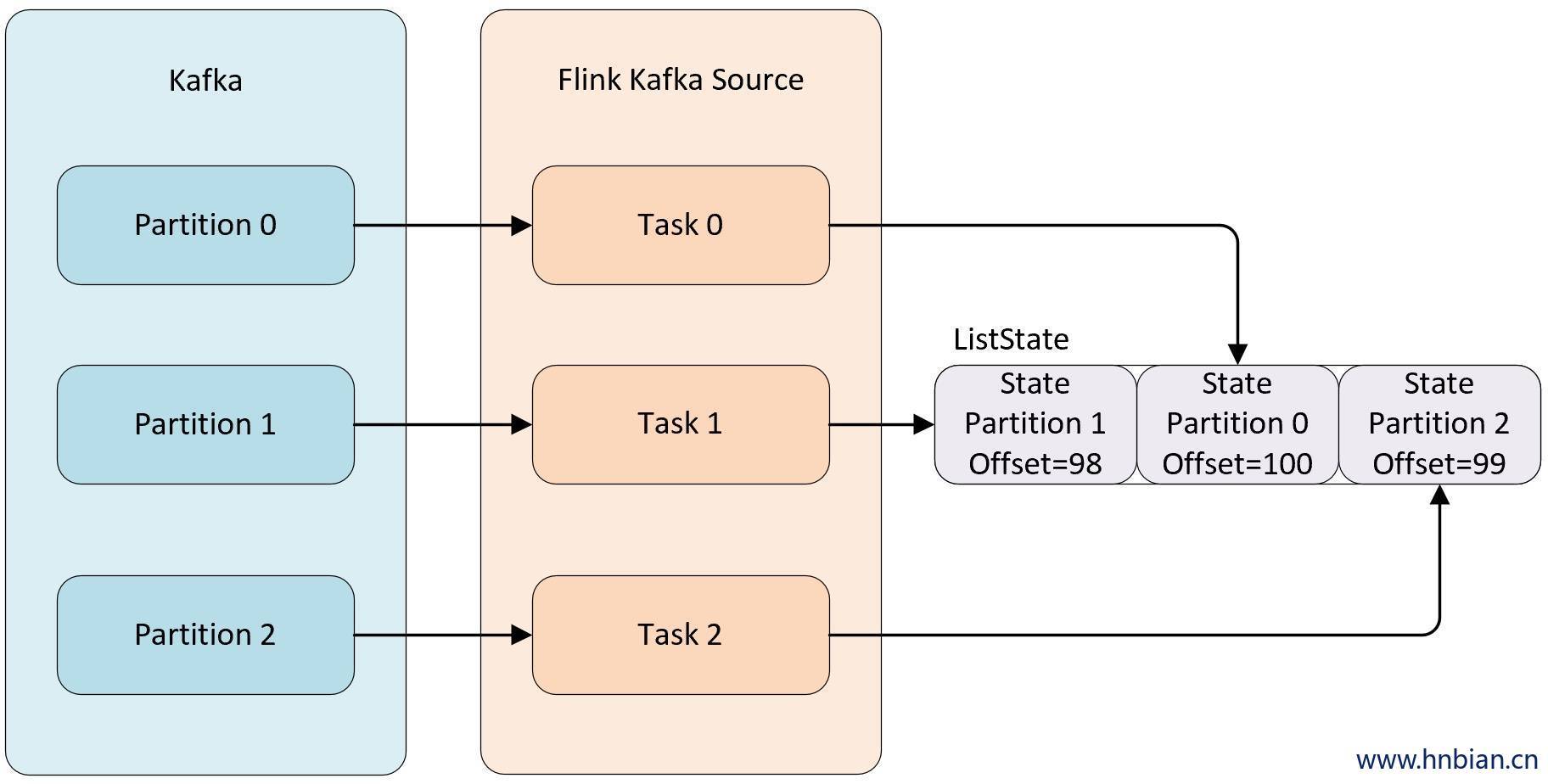
例如当消费 kafka 数据的 Kafka Source 并行度为 3 时,默认每个并行度都是从一个 Kafka 的 topic 的某个分区中消费数据,而每个 kafka Source 为了保证在极端情况下也不丢失数据,就不能将 partition 对应的 offset 保存到默认的 zookeeper 中,而是需要将这些数据保存在状态中,自己来维护这部分数据。当并行度发生调整时,需要在 Operator 的并行度上重新分配状态。
|
||
|
||
在流数据开发的大多数场景中,我们都不需要使用 Operator State ,Operator State 的实现主要是针对一些没有 Keyed 操作的 Source 和 Sink 而设计的
|
||
|
||
Operator State 的作用范围限定为算子任务。这意味着由同一并行任务所处理的所有数据都可以访问到相同的状态,状态对于同一任务而言是共享的。算子状态不能由相同或不同算子的另一个任务访问。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
Flink 为算子状态提供三种基本数据结构:
|
||
|
||
- 列表状态( List state ):状态是一个 **可序列化** 对象的集合 `List`,彼此独立,方便在改变并发后进行状态的重新分派。这些对象是重新分配 non-Keyed State 的最细粒度。根据状态的不同访问方式,有如下两种重新分配的模式:
|
||
|
||
- **Even-split redistribution:** 每个算子都保存一个列表形式的状态集合,整个状态由所有的列表拼接而成。当作业恢复或重新分配的时候,整个状态会按照算子的并发度进行均匀分配。比如说,算子 A 的并发读为 1,包含两个元素 `element1` 和 `element2`,当并发读增加为 2 时,`element1` 会被分到并发 0 上,`element2` 则会被分到并发 1 上。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
- **Union redistribution:** 每个算子保存一个列表形式的状态集合。整个状态由所有的列表拼接而成。作业恢复或重新分配时,每个算子都将获得所有的状态数据。Union redistribution 模式下 checkpoint metadata会存储每个operator 的 subTask 的offset信息。如果List State的基数较大时,不要使用这种方式的redistribution。因为容易引起OOM。
|
||
|
||
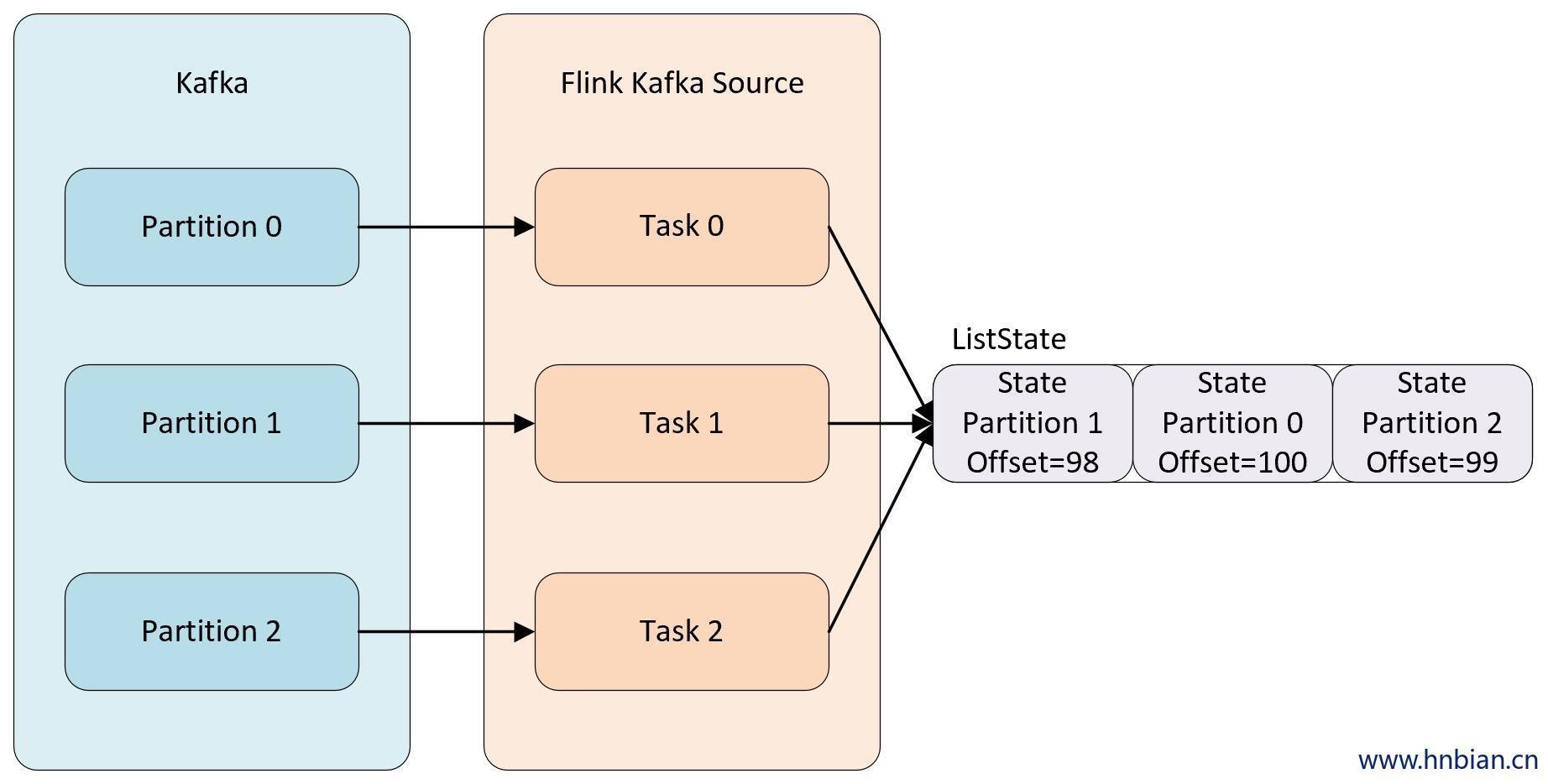
|
||
|
||
- 调用不同的获取状态对象的接口,会使用不同的状态分配算法。比如 `getUnionListState(descriptor)` 会使用 union redistribution 算法, 而 `getListState(descriptor)` 则简单的使用 even-split redistribution 算法。
|
||
|
||
- 当初始化好状态对象后,我们通过 `isRestored()` 方法判断是否从之前的故障中恢复回来,如果该方法返回 `true` 则表示从故障中进行恢复,会执行接下来的恢复逻辑。
|
||
|
||
- 广播状态( Broadcast state ):如果一个算子有多项任务,而它的每项任务状态又都相同,那么这种特殊情况最适合应用广播状态。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 状态后端和checkpoint
|
||
|
||
- 状态后端是保存到本地的状态。
|
||
- checkpoint是将状态定时备份到第三方存储,比如hdfs,obs上面,方便在作业重新运行的时候恢复数据。
|
||
|
||
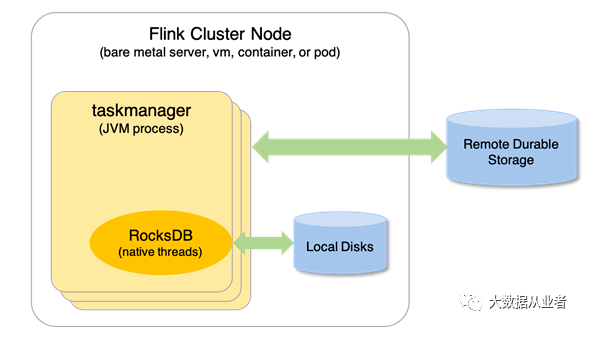
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 状态后端相关配置
|
||
|
||
| 配置名称 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| **state.backend** | - | 建议配置为rocksdb |
|
||
| state.backend.latency-track.keyed-state-enabled | false | 是否跟踪keyed state operations的延时,建议不要开启 |
|
||
| state.backend.latency-track.sample-interval | 100 | 跟踪耗时超过100ms的operations |
|
||
| state.backend.latency-track.history-size | 128 | 跟踪耗时较高operation的个数 |
|
||
| table.exec.state.ttl | - | 状态后端ttl时间,一般用于join场景下,防止状态后端过大导致作业失败 |
|
||
|
||
|
||
# checkpoint 相关配置
|
||
|
||
| 配置名称 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
||
| **execution.checkpointing.interval** | - | checkpoint的触发的时间,每个一段时间都会触发checkpoint。建议一般配置为1-10min左右 |
|
||
| **execution.checkpointing.mode** | EXACTLY_ONCE | EXACTLY_ONCE:保证精确一次;<br> AT_LEAST_ONCE:至少一次。建议EXACTLY_ONCE |
|
||
| **state.backend.incremental** | false | 是否开启增量checkpoint,建议开启 |
|
||
| **execution.checkpointing.timeout** | 10min| checkpoint的超时时间,建议设置长一点,30min左右 |
|
||
| **execution.checkpointing.unaligned.enabled** | false | 是否启用非对齐checkpoint,建议不开启 |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.unaligned.forced | false | 是否强制开启非对齐checkpoint |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.max-concurrent-checkpoints | 1 | 同时进行checkpoint的最大次数 |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.min-pause | 0 | 两个checkpoint之间的最小停顿时间 |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.tolerable-failed-checkpoints | - | 可容忍的checkpoint的连续故障数目 |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.aligned-checkpoint-timeout | 0 | 对齐checkpoint超时时间 |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.alignment-timeout | 0 | 参考:execution.checkpointing.aligned-checkpoint-timeout <span style="color:red;">(已经过期)</span> |
|
||
| execution.checkpointing.force | false | 是否强制检查点<span style="color:red;">(已经过期)</span> |
|
||
| state.checkpoints.num-retained | 1 | checkpoint 保存个数 |
|
||
| state.backend.async | true | 是否开启异步checkpoint <span style="color:red;">(已经过期)</span> |
|
||
| state.savepoints.dir | - | savepoints存储文件夹 |
|
||
| state.checkpoints.dir | - | checkpoint存储文件夹 |
|
||
| state.storage.fs.memory-threshold | 20kb | 状态文件的最小大小 |
|
||
| state.storage.fs.write-buffer-size | 4 * 1024 | 写入文件系统的检查点流的写入缓冲区的默认大小。 |
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## RocksDb相关配置
|
||
|
||
| 配置项名称 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|
||
|----|----|----|
|
||
| state.backend.rocksdb.checkpoint.transfer.thread.num | 4 | 用于上传和下载文件的线程数目 |
|
||
| state.backend.rocksdb.write-batch-size | 2mb | Rocksdb写入时消耗的最大内存 |
|
||
| state.backend.rocksdb.predefined-options | DEFAULT | `DEFAULT`:所有的RocksDb配置都是默认值。 <br>`SPINNING_DISK_OPTIMIZED`:在写硬盘的时候优化RocksDb参数 <br>`SPINNING_DISK_OPTIMIZED_HIGH_MEM`: 在写入常规硬盘时优化参数,需要消耗更多的内存<br> `FLASH_SSD_OPTIMIZED`:在写入ssd闪盘时进行优化。 |
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 状态后端实现
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
StateBackend实现类图,在1.17版本中,部分状态后端已经过期,比如:~~MemoryStateBackend~~、~~RocksDBStateBackend~~、~~FsStateBackend~~等。
|
||
|
||
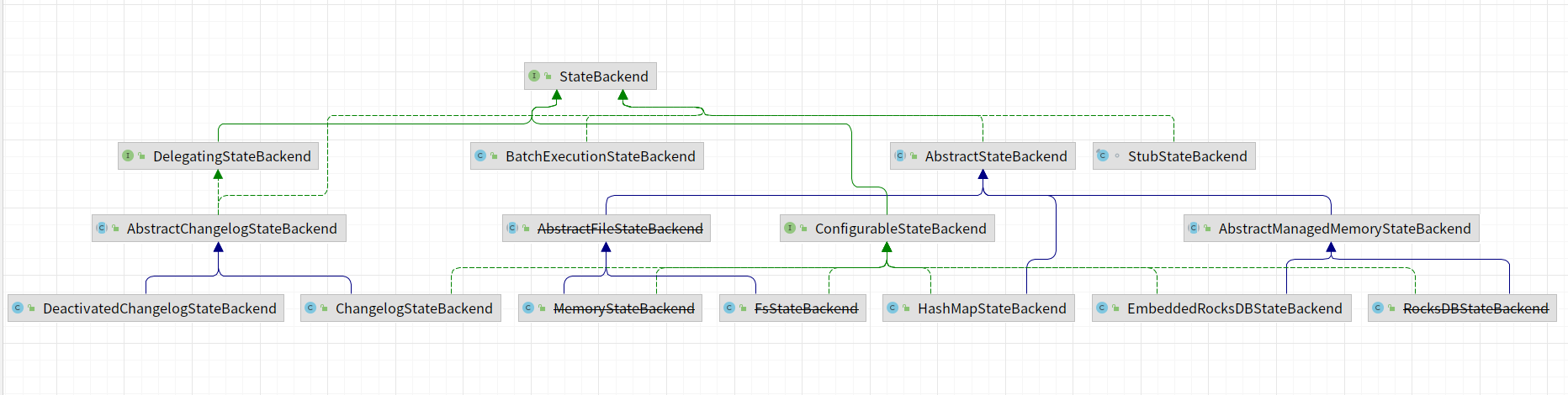
|
||
|
||
去除掉已经过期的状态后端剩余的如下所示:
|
||
|
||
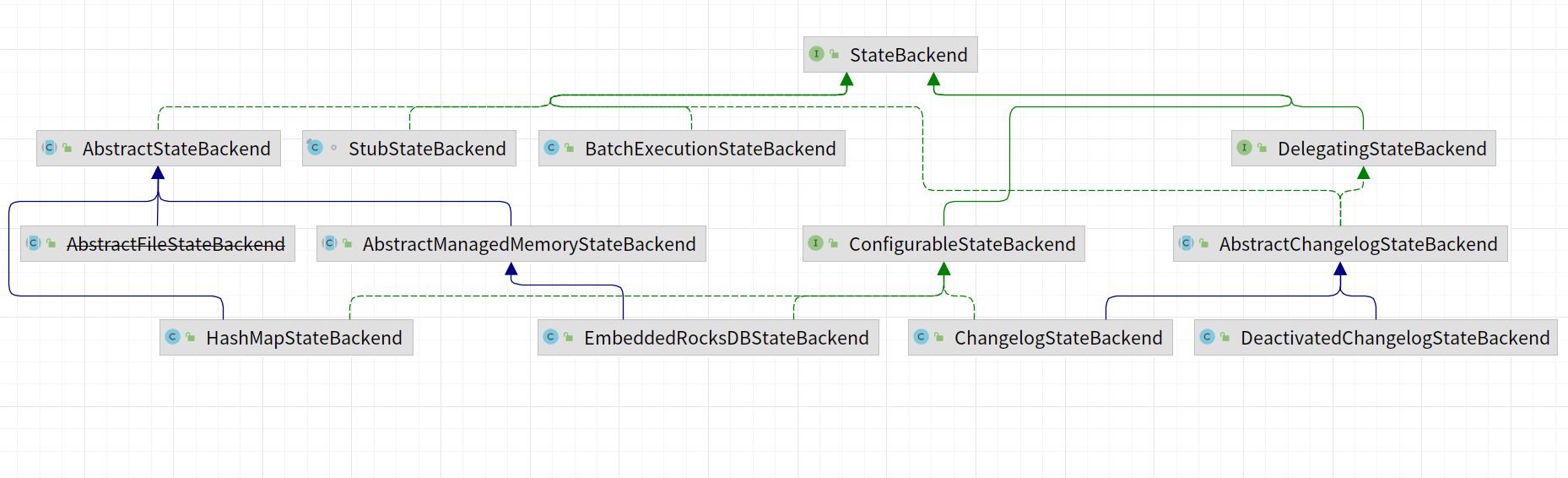
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## HashMapStateBackend
|
||
|
||
在TaskManager的内存当中保存作业的状态后端信息,如果一个TaskManager并行执行多个任务时,所有的聚合信息都要保存到当前的TaskManager内存里面。数据主要以Java对象的方式保存在堆内存当中。Key/value 形式的状态和窗口算子会持有一个 hash table,其中存储着状态值、触发器。
|
||
|
||
内存当中存储格式定义如下:
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
/** So that we can give out state when the user uses the same key. */
|
||
private final HashMap<String, InternalKvState<K, ?, ?>> keyValueStatesByName;
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
### 适用场景
|
||
|
||
- 有较大 state,较长 window 和较大 key/value 状态的 Job。
|
||
- 所有的高可用场景。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
建议同时将 [managed memory](https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.14/zh/docs/deployment/memory/mem_setup_tm/#managed-memory) 设为0,以保证将最大限度的内存分配给 JVM 上的用户代码。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## EmbeddedRocksDBStateBackend
|
||
|
||
将正在于行的作业的状态保存到RocksDb里面。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 创建KeyedStateBackend
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
1. 加载`RocksDB JNI library`相关Jar包。
|
||
|
||
2. 申请RocksDB所需要的内存。核心代码在SharedResources类当中的getOrAllocateSharedResource函数。在申请资源之前会先加锁,在加锁成功会申请所需要的资源。加锁代码如下:
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
```java
|
||
try {
|
||
lock.lockInterruptibly();
|
||
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
|
||
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
|
||
throw new MemoryAllocationException("Interrupted while acquiring memory");
|
||
}
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
在申请资源之前需要根据类型判断是否已经申请了资源,如果已经申请了资源就不会重新申请,没有则需要申请。申请的代码如下所示:
|
||
|
||
````java
|
||
private static <T extends AutoCloseable> LeasedResource<T> createResource(
|
||
LongFunctionWithException<T, Exception> initializer, long size) throws Exception {
|
||
|
||
final T resource = initializer.apply(size);
|
||
return new LeasedResource<>(resource, size);
|
||
}
|
||
````
|
||
|
||
3. 创建resourceContainer,包含预先定义好的RocksDB优化选项等。
|
||
|
||
````java
|
||
private RocksDBResourceContainer createOptionsAndResourceContainer(
|
||
@Nullable OpaqueMemoryResource<RocksDBSharedResources> sharedResources,
|
||
@Nullable File instanceBasePath,
|
||
boolean enableStatistics) {
|
||
|
||
return new RocksDBResourceContainer(
|
||
configurableOptions != null ? configurableOptions : new Configuration(),
|
||
predefinedOptions != null ? predefinedOptions : PredefinedOptions.DEFAULT,
|
||
rocksDbOptionsFactory,
|
||
sharedResources,
|
||
instanceBasePath,
|
||
enableStatistics);
|
||
````
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
4. 初始化RocksDBKeyedStateBackend,会从目录里面加载数据到RocksDB里面。
|
||
|
||
````java
|
||
restoreOperation =
|
||
getRocksDBRestoreOperation(
|
||
keyGroupPrefixBytes,
|
||
cancelStreamRegistry,
|
||
kvStateInformation,
|
||
registeredPQStates,
|
||
ttlCompactFiltersManager);
|
||
RocksDBRestoreResult restoreResult = restoreOperation.restore();
|
||
db = restoreResult.getDb();
|
||
defaultColumnFamilyHandle = restoreResult.getDefaultColumnFamilyHandle();
|
||
````
|
||
|
||
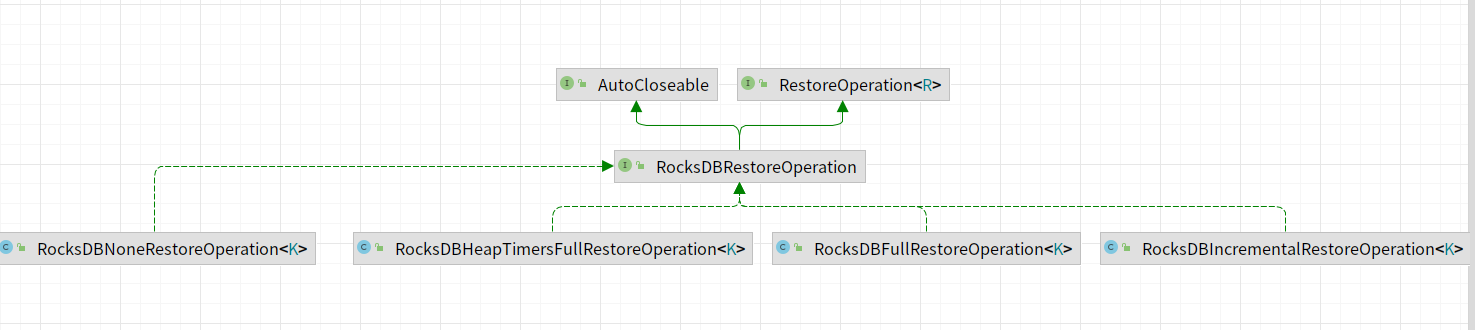
restoreOperation实现类图如下所示,主要包含如下的实现类。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## ChangelogStateBackend
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## DeactivatedChangelogStateBackend
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
# 常见报错
|
||
|
||
## The maximum number of queued checkpoint requests exceeded
|
||
|
||
未完成的Checkpoint排队超过了1000个。需要查看作业是否存在被压等。一般情况下作业被压会导致checkpoint失败。
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Periodic checkpoint scheduler is shut down
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## The minimum time between checkpoints is still pending
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Not all required tasks are currently running
|
||
|
||
部分算子任务已经完成,但是如果在维表join场景下,flink 1.13版本之前可能无法恢复checkpoint
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## An Exception occurred while triggering the checkpoint.
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Asynchronous task checkpoint failed.
|
||
|
||
|
||
## The checkpoint was aborted due to exception of other subtasks sharing the ChannelState file
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint expired before completing
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint has been subsumed
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint was declined
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint was declined (tasks not ready)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint was declined (task is closing)
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint was canceled because a barrier from newer checkpoint was received
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Task received cancellation from one of its inputs
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint was declined because one input stream is finished
|
||
|
||
|
||
## CheckpointCoordinator shutdown
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Checkpoint Coordinator is suspending
|
||
|
||
|
||
## FailoverRegion is restarting
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Task has failed
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Task local checkpoint failure
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Unknown task for the checkpoint to notify
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Failure to finalize checkpoint
|
||
|
||
|
||
## Trigger checkpoint failure
|
||
|
||
|
||
|