4.7 KiB
4.7 KiB
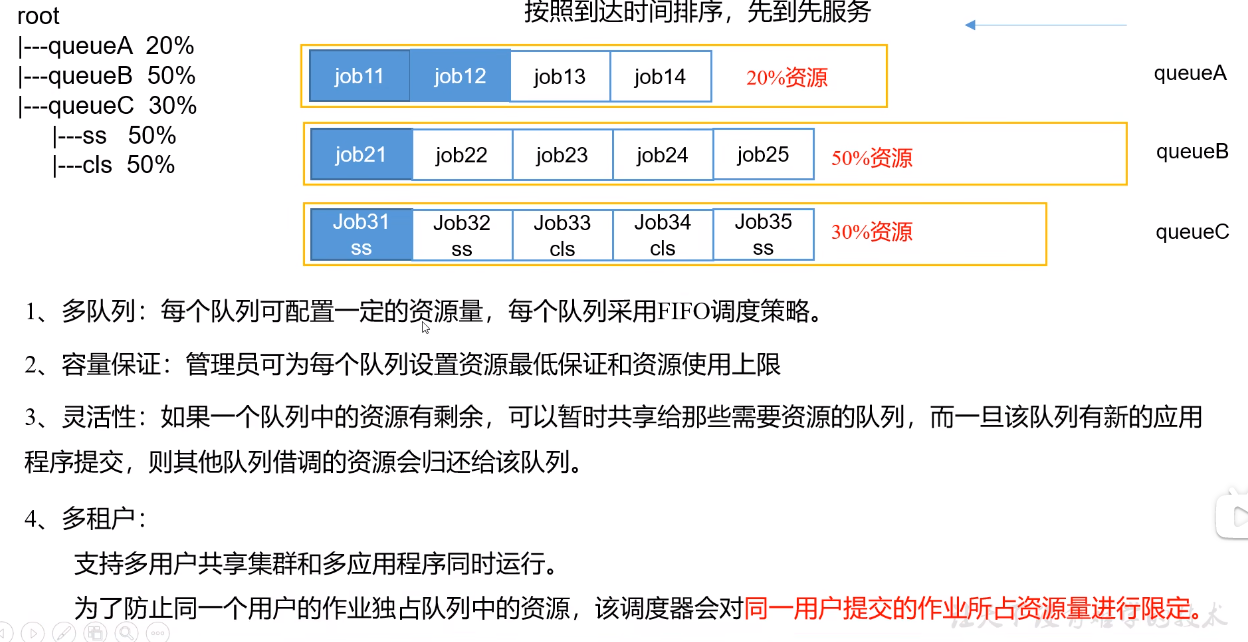
简介
源码解析
Capacity 调度器的核心类是CapacityScheduler。在初始化CapacityScheduler的时候,在构造函数initAsyncSchedulingProperties,里面会初始化调度器相关。 核心类是AsyncSchedulingConfiguration,主要内容总结为:初始化异步调度器线程AsyncScheduleThread,可以初始化多个,调度支持多线程。
AsyncScheduleThread继承自Thread,核心是循环调度,调度的核心函数为schedule。
schedule函数
一般情况下,满足下面条件的节点不会被分配资源:
- 心跳超时的节点,心跳超时的节点一般认为是可能已经dead了。为了可靠性考虑,不给此类节点分配Container。
- 当前节点的状态不为RUNNING状态,不为RUNNING状态的节点是异常的,不能分配节点。
上述判断的核心实现函数为shouldSkipNodeSchedule。
资源分配方式
资源分配方式分为:
- 按照节点分配资源
- 按照标签进行分配
按照节点分配资源
- 随机产生一个随机数,范围是0 ~ allNode.size。
- 优先从下标为[start, end)的节点中分配资源。
- 再次从下标为[0, start)的节点中分配资源。
代码主要流程如下:
int start = random.nextInt(nodeSize);
boolean printSkippedNodeLogging = isPrintSkippedNodeLogging(cs);
// Allocate containers of node [start, end)
for (FiCaSchedulerNode node : nodes) {
if (current++ >= start) {
if (shouldSkipNodeSchedule(node, cs, printSkippedNodeLogging)) {
continue;
}
cs.allocateContainersToNode(node.getNodeID(), false);
}
}
current = 0;
// Allocate containers of node [0, start)
for (FiCaSchedulerNode node : nodes) {
if (current++ > start) {
break;
}
if (shouldSkipNodeSchedule(node, cs, printSkippedNodeLogging)) {
continue;
}
cs.allocateContainersToNode(node.getNodeID(), false);
}
按照标签进行分配
- 随机产生一个随机数,范围是0 ~ partitions.size。
- 优先从下标为[start, end)的标签中分配资源。
- 再次从下标为[0, start)的标签中分配资源。
int partitionSize = partitions.size();
// First randomize the start point
int start = random.nextInt(partitionSize);
// Allocate containers of partition [start, end)
for (String partition : partitions) {
if (current++ >= start) {
CandidateNodeSet<FiCaSchedulerNode> candidates =
cs.getCandidateNodeSet(partition);
if (candidates == null) {
continue;
}
cs.allocateContainersToNode(candidates, false);
}
}
current = 0;
// Allocate containers of partition [0, start)
for (String partition : partitions) {
if (current++ > start) {
break;
}
CandidateNodeSet<FiCaSchedulerNode> candidates =
cs.getCandidateNodeSet(partition);
if (candidates == null) {
continue;
}
cs.allocateContainersToNode(candidates, false);
}
资源分配具体实现
资源分配的核心实现函数为allocateContainersToNode。首先检查当前节点是否存在运行时预留的资源,优先处理运行时预留资源。
运行时预留
资源分配
对于可用资源和可kill的资源加和小于最小资源的时候,不会再进行资源分配或者资源预留了,因为资源肯定是不足的。
资源存在的场景需要进行资源分配或者资源预留。核心实现函数为allocateOrReserveNewContainers。优先尝试从没有标签的节点分配资源。再没有分配到资源之后,最后尝试按照资源标签进行分配。
从没有资源标签的节点分配的函数入口如下,资源分配都是从根队列开始分配的。
CSAssignment assignment = getRootQueue().assignContainers(
getClusterResource(), candidates, new ResourceLimits(labelManager
.getResourceByLabel(candidates.getPartition(),
getClusterResource())),
SchedulingMode.RESPECT_PARTITION_EXCLUSIVITY);
assignment.setSchedulingMode(SchedulingMode.RESPECT_PARTITION_EXCLUSIVITY);
submitResourceCommitRequest(getClusterResource(), assignment);
对于包含资源标签的节点分配资源实现如下:
assignment = getRootQueue().assignContainers(getClusterResource(),
candidates,
// TODO, now we only consider limits for parent for non-labeled
// resources, should consider labeled resources as well.
new ResourceLimits(labelManager
.getResourceByLabel(RMNodeLabelsManager.NO_LABEL,
getClusterResource())),
SchedulingMode.IGNORE_PARTITION_EXCLUSIVITY);
assignment.setSchedulingMode(SchedulingMode.IGNORE_PARTITION_EXCLUSIVITY);
submitResourceCommitRequest(getClusterResource(), assignment);
assignContainers
根队列的实现类为AbstractParentQueue.java。低版本的实现类为ParentQueue.java